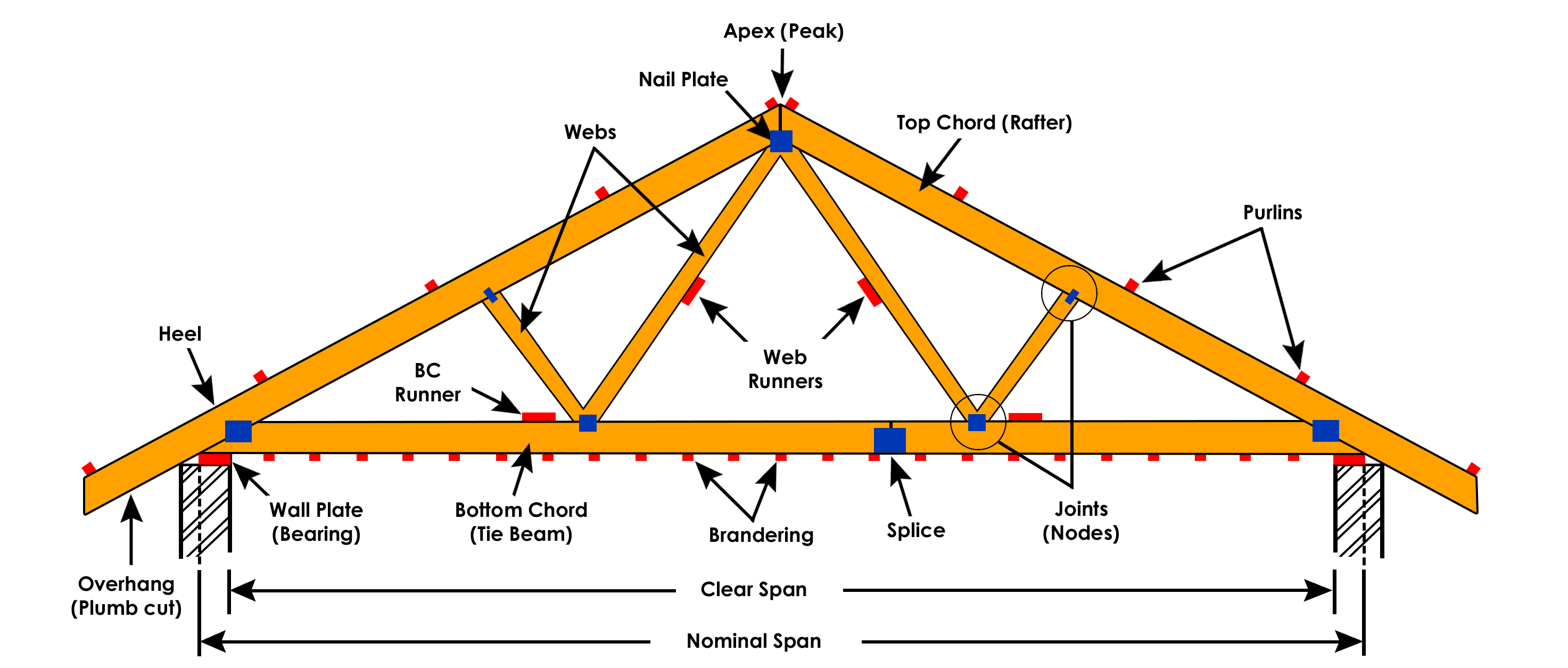
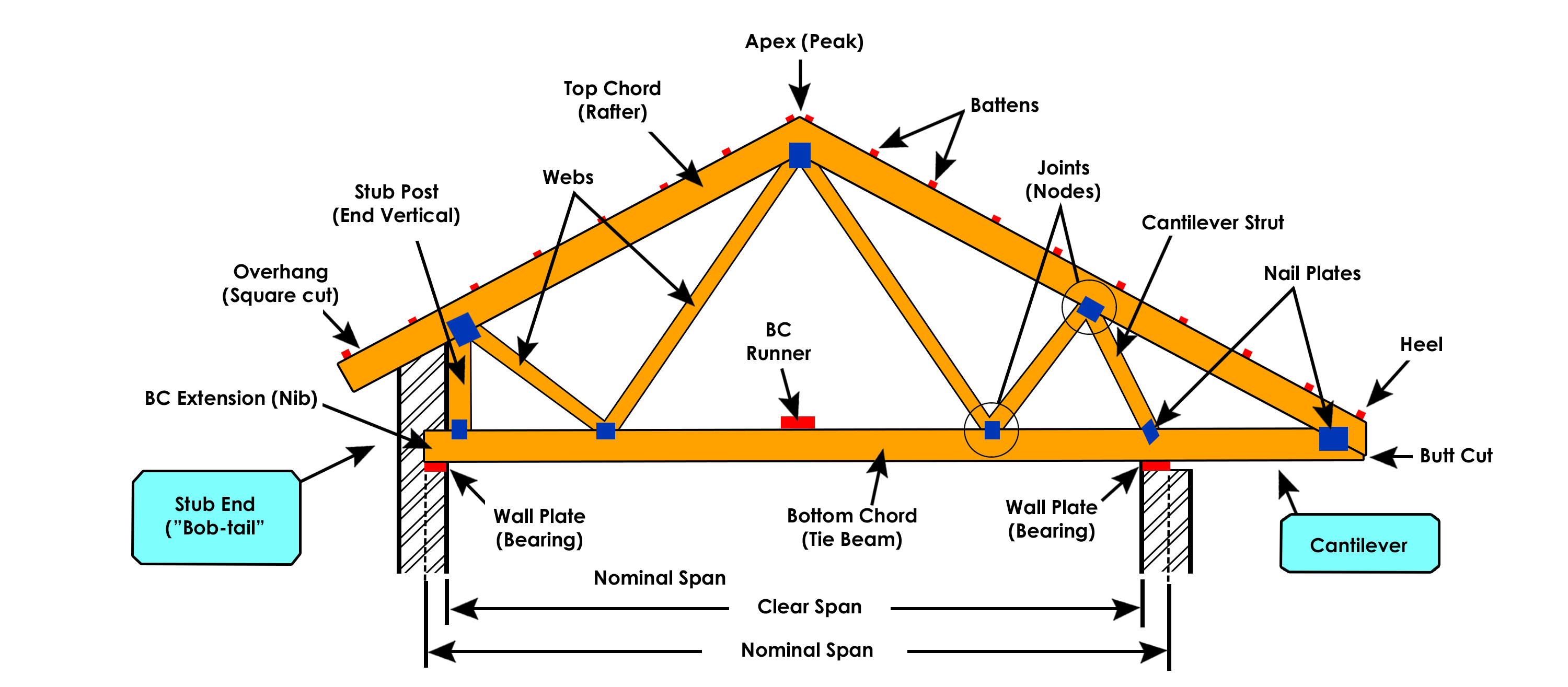
A roof truss is a structural unit designed to frame a roof and to support the roof material, interior ceiling, insulation, and forces caused by snow, rain, and wind. A roof truss is supported by the exterior walls and span the width of the building.
Components of Roof Truss
A common truss is recognizable by its triangular shape and is most often used in roof construction. The following are various components of a roof truss.
- Principal rafter or Top Chord
- Bottom chord or main tie
- Ties
- Struts
- Sag tie
- Purlins
- Rafters
- Ridge line
- Eaves
- Panel points
- Roof covering
- Shoe angle
- Base plate, anchor plate and anchor bolts.
Types of Roof Trusses
There are many types of trusses available for residential, commercial and industrial building construction. Each type has specific design considerations and advantages and disadvantages. Here are most popular roof trusses widely used.
- King Post Truss
- Pratt Truss
- Queen Post Truss
- Howe Truss
- Fan Truss
- North Light Roof Truss
- Quadrangular Roof Trusses
- Parallel Chord Roof Truss
- Scissor Roof Truss
- Raised Heel Roof Truss
Roof Truss Advantages
- Roof trusses can save on-site costs.
- Better project cost control, with component costs known in advance
- Better cash flow with earlier occupancy due to reduced on-site labour
- Faster shell completion time
- Using trusses of smaller dimension lumber, in place of beams and columns
- Greater flexibility in locating plumbing, duct work, and electrical wiring
- Floor plan freedom in locating interior partitions often without additional support required
- Pre-determined, pre-engineered truss system
- Fewer pieces to handle and reduced installation time
- Wide 3-1/2” nailing surface for easy floor deck application
- Eliminate notching and boring joists for electrical wiring and plumbing
- Floor trusses offer better availability and less in-place cost than 2×8 or 2×10 joists
- Factory-manufactured components to exact span requirements
- Reduced HVAC, plumbing, and electrical subcontractor time on job
- No column pads to pour, no steel beams and posts to place
- Job site material pilferage and cutting waste reduced
Roof Truss Disadvantages
- Roof trusses have a series of supporting members that limit the use of attic space.
- Large trusses require a crane